From December 1st 2015 to November 30th 2018, MultiMed Engineers participated in the City4Age Project — Elderly-friendly City services for active and healthy ageing.
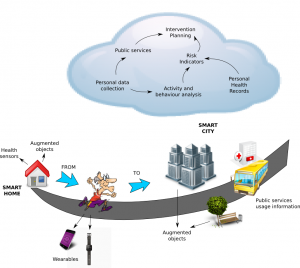 City4Age aimed to activate urban communities to facilitate the role of social/health services and of families in dealing with mild cognitive impairments and frailty in the elderly population. The challenge has been to demonstrate that cities play a pivotal role in the unobtrusive collection of “more data” on individual behaviours, and with “increased frequency”. This can then greatly improve the early detection of risks through the timely analysis of changes in the behaviours and the design of effective interventions for countering these risks.
City4Age aimed to activate urban communities to facilitate the role of social/health services and of families in dealing with mild cognitive impairments and frailty in the elderly population. The challenge has been to demonstrate that cities play a pivotal role in the unobtrusive collection of “more data” on individual behaviours, and with “increased frequency”. This can then greatly improve the early detection of risks through the timely analysis of changes in the behaviours and the design of effective interventions for countering these risks.
The core objective of City4Age has been to enable Ambient Assisted Cities or Age-friendly Smart Cities, where the urban communities of elderly people are provided with a range of ICT tools and services that — in a completely unobtrusive manner — will improve the early detection of risks related to cognitive impairments and frailty, while they are at home or in the move within the city.
The second objective has been to provide a range of associated tools and services which — supporting appropriate interventions — will mitigate the detected risks.
The final objective of City4Age has been to define a model to provide sustainability and extensibility to the offered services and tools by addressing the unmet needs of the elderly population in terms of (i) detecting risks related to other health type problems, (ii) stimulating and providing incentives to remain active, involved and engaged, (iii) creating an ecosystem for multisided market by matching needs and their fulfillments, (iv) contributing to the design and operation of the ultimate Age-friendly City, where the city itself provides support for detecting risks and providing interventions to those affected by mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and frailty.
To achieve these objectives City4Age built on:
- behavioural, sociological and clinical research on “frailty” and MCI in the elderly population;
- state of art ICT technology (i) for “sensing” personal data and exposing them as linked open data, (ii) for designing the algorithms and the API’s to extract relevant behaviour changes and correlated risks, and (iii) for designing interventions to counter the risks
- stakeholder engagement in order to be driven by relevant user needs to ensure end-user acceptance
In addition to MultiMed Engineers, the Project Consortium includes Politecnico di Milano (IT, coordinator), Universidad de la Iglesia de Deusto (ES), GeoMobile GmbH (DE), Comune di Lecce (IT), Universidad Politecnica de Madrid (ES), Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid (ES), DAEM S.A. (EL), Università di Pavia (IT), Athens Technological Centre S.A. (EL), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique – IPAL lab (FR), BELIT d.o.o. (RS), Università del Salento (IT), University College London – Centre for Behaviour Change (UK) and Birmingham City Council (UK).
Testbeds have been located in the cities of Athens, Birmingham, Lecce, Madrid, Montpellier, and Singapore.
MultiMed Engineers coordinated the activities of WP2 (Requirements of the risk detection system), participated in the Innovation management and Quality management activities and supported the implementation of the Project’s testbeds.

This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 689731
 MultiMed Engineers
MultiMed Engineers