Since September 1st 2022, MultiMed Engineers participates in the IDEA4RC Project — Intelligent Ecosystem to improve the governance, the sharing, and the re-use of health Data for Rare Cancers.
Despite their relevance, rare cancers in general get less scientific consideration and financial support than their more common counterparts. Carrying out clinical studies is difficult, because of the small number of sample populations. Therefore, clinical evidence is more difficult to build, clinical management is more complex, including accessing clinical skills and proper treatments, and shortage of accessible cancer registries and data is a fundamental obstacle.
There is a wide consensus that especially primary treatment of rare cancers should be centralized to reference centres and/or to collaborative health networks with multidisciplinary, highly specific expertise. Clinical and translational research too would need a high level of centralization and international collaboration. EURACAN – which focusses on rare adult solid cancers – is the largest ERN for rare cancers, addressing 10 out of the 12 families of rare cancers (75% of all rare cancers) and is representative of the European healthcare landscape. It currently includes about 70 health care providers across 17 EU Member States of different populations and socio-economic context.
In this context, IDEA4RC leverages on EURACAN’s wealth of data, on one side, and on emerging interoperability technologies and AI approaches for distributed data integration, federated analysis, and knowledge extraction from existing structured (e.g., EHRs, e-CRFs, Registries) and unstructured (e.g., clinician notes, image reports, pathology reports) health data on the other side, to improve the delivery of care, facilitate patients’ information and advance clinical and epidemiological research in rare cancers. The project ambition is to establish the framework for a first-in-the-field European Data Ecosystem for Rare Cancers, spanning multiple sources in multiple EU countries and supported by (i) a federation of interoperability “capsules” based on FHIR APIs; (ii) AI tools for multi-language data processing and analysis; (iii) a Multimodal Data Navigator to assist clinicians and researchers in finding and accessing available data of stipulated quality; and (iii) modern trust-building technologies (e.g. blockchain) to orchestrate data governance and incentivize data sharing and altruism. The developed tools will be experienced by relevant “data (re-)use pilot cases” across 11 reference Centers of the ERN EURACAN. The “Rare Cancer Data Ecosystem” realized in the project will improve the quality of care, patients’ access to optimal diagnosis and treatment, and will increase knowledge on rare cancers, advancing clinical and epidemiological research, so that ultimately all patients have equal access to high quality specialist care all over EU, in compliance with principle 16 of the European Pillar of Social Rights.
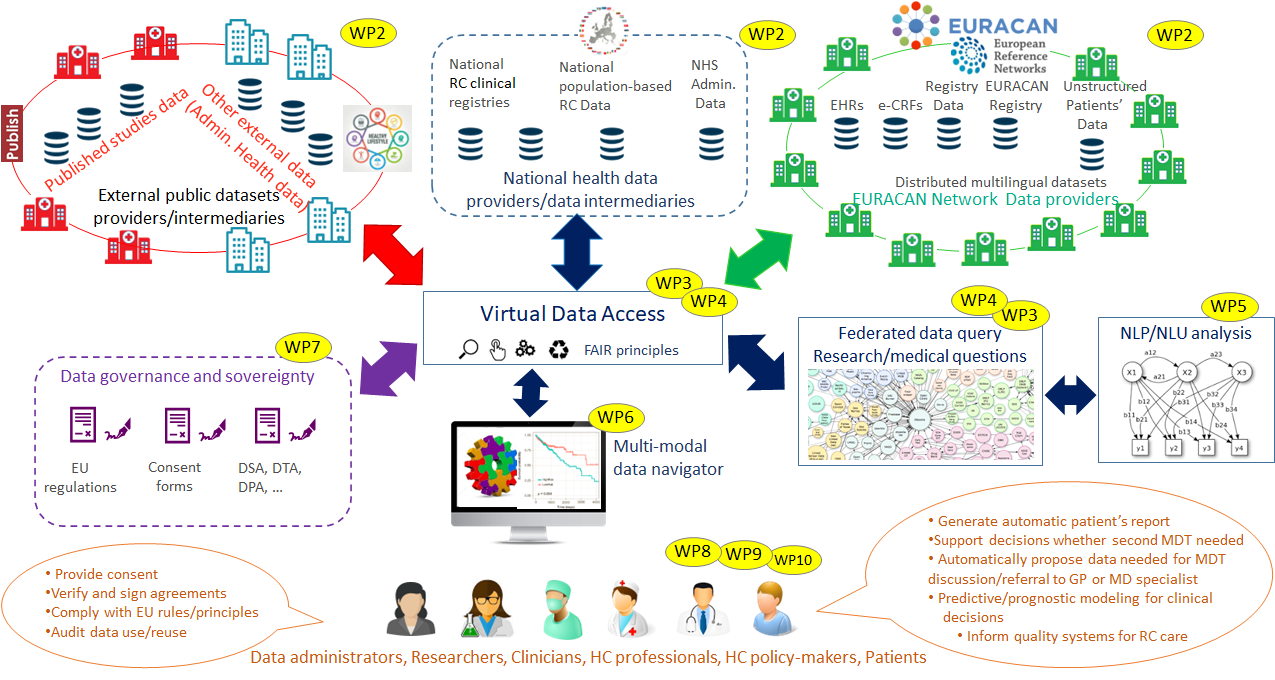
The IDEA4RC Race Cancer Data Ecosystem concept
Building on the principles of the European Data Strategy, the Rare Cancer Data Ecosystem concept proposed by IDEA4RC (Figure above) will unite available data sources and equip them with strong data governance controls to lay down the basis for an embryonic data space for rare cancers, initially revolving around the ERN EURACAN and founded on the following pillars:
- Data are voluntary shared by data holders with relevant stakeholders (initially within the EURACAN network and subsequently beyond), based on clear and fair incentivization mechanisms that encourage data access and data reuse.
- Any data holder is free to participate in the Ecosystem as much as it would (respecting its data sovereignty entitlements) and as much as it could (supporting it with specific interoperability tools).
- EU regulations and principles will be interwoven into the very fabric of the Data Ecosystem, to ensure regulatory compliance, protection of patients and citizens’ rights, and to generate trust.
- Unstructured, natural language data are made first citizens in the Rare Cancer Data Ecosystem, on a par with structured data.
- Metadata are curated and leveraged to create “virtual views” that pool existing “data molecules”, accessible from data holders participating in the system, in order to offer a transparent, uniform access over richer and larger datasets that can be synergistically constructed on top of them. This is the central element for offering a sound solution to the data scarcity issue that plagues the race cancer domain.
- Guidance is provided for finding the optimal datasets, among the many that can be virtually reconstructed and accessed as per previous bullet. Such guidance is embodied in a multimodal data navigator, driven by “meta-knowledge” that includes not only technical information needed to drive interoperability, but also data quality as well as data sovereignty meta-information, to ensure that retrieved datasets are of the right value and that their access is respectful of relevant data governance rules (GDPR provisions, data subject consent, data sharing/transfer agreements in place, etc.) in such a way that they get immediate clearance for effective use and/or reuse for the cases at hand.
The Project Consortium is coordinated by Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori di Milano (IT) and includes — in addition to MultiMed Engineers — the following Partners: Universidad de la Iglesia de Deusto (ES), Universidad Politecnica de Madrid (ES), HL7 International (BE), European Center for Certification and Privacy (LU), Engineering Ingegneris Informatica (IT), Ethniko Kentro Erevnas kai Technologikis Anaptyxis CERTH (EL), University of Utrecht (NL), DIGital Institute for Cancer Outcomes Research (BE), Fondazione Bruno Kessler (IT), Stchting Integraal Kankercentrum zuid IKNL (NL), Centre de lutte contre le cancer Léon Berard (FR), Assistance publique – Hôpitaux de Paris (FR), Fundación Jimenez Diaz University Hospital (ES), Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg VGR (SE), Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Institute and Oncology Centre (PL), Motol University Hospital (CZ), Oslo University Hospital (NO), Masaryk Memorial Cancer Institute (CZ), Clininote (PL), Fundación Profesor Novoa Santos (ES), TNO (NL), INFERENZE (IT), Universitätsklinik Essen (DE).
MultiMed Engineers, which participated in the overall conception of the Project, is involved in the following phases of the Workplan:
- Elicitation of User Requirements (through the methodology of User Stories) and follow up of their implementation in the system architecture
- Coordination of the technical deployment of the data ecosystem, to ensure its validation through the execution of planned data (re-)use pilot cases
- Supporting the ecosystem enlargement process consistently with the project Workplan and in an economically sustainable way
- Participanting in project results’ dissemination and exploitation.
Project Website: https://www.idea4rc.eu/

This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101057048
 MultiMed Engineers
MultiMed Engineers